Gingivitis and Gum Disease
We’ve been told our entire lives to brush our teeth every day, and this daily activity can be rather laborious for many of us. But why is it so important, and what will happen if we skip a day or two?
The mouth harbors billions of bacteria that cling to each tooth. According to the U.S. National Library of Medicine, over 700 bacterial species have been identified inside an oral cavity. Many of these strains of bacteria are harmless, but some can cause damage, such as tooth cavities and gum disease.
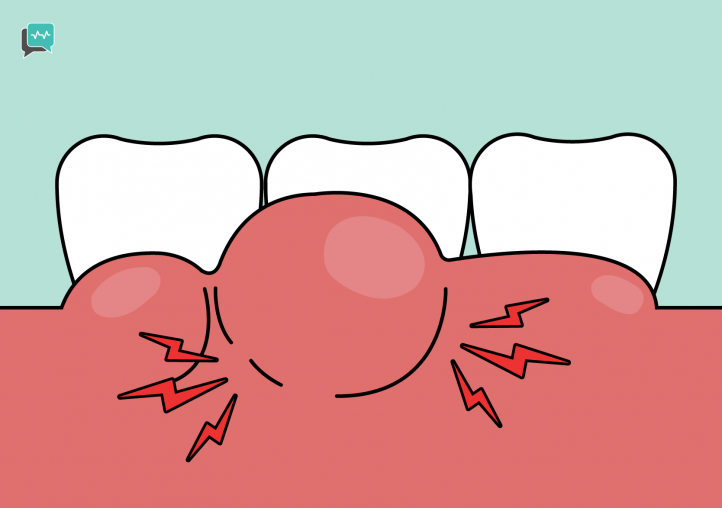
Gum disease, which includes gingivitis and periodontitis, is infection and inflammation of the tissues that support the teeth, and a leading cause of tooth loss.
Recent studies have also found that the effects of gum disease are not always confined to the oral cavity. As it advances, those affected may be at a higher risk of getting other serious health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory diseases, pregnancy related complications and dementia.
Therefore, it is important to be disciplined with the oral care that is generally practiced at home. This includes brushing the teeth twice a day, as well as cleaning in between the teeth (using dental floss or interdental brushes), and this should be carried out daily. Regular dental check-ups and professional teeth cleaning are also an important component of oral care, as they can detect and manage gum disease and tooth decay early enough to be managed effectively. The effects of all this go a long way in improving the overall oral as well as general health.
What is gingivitis?
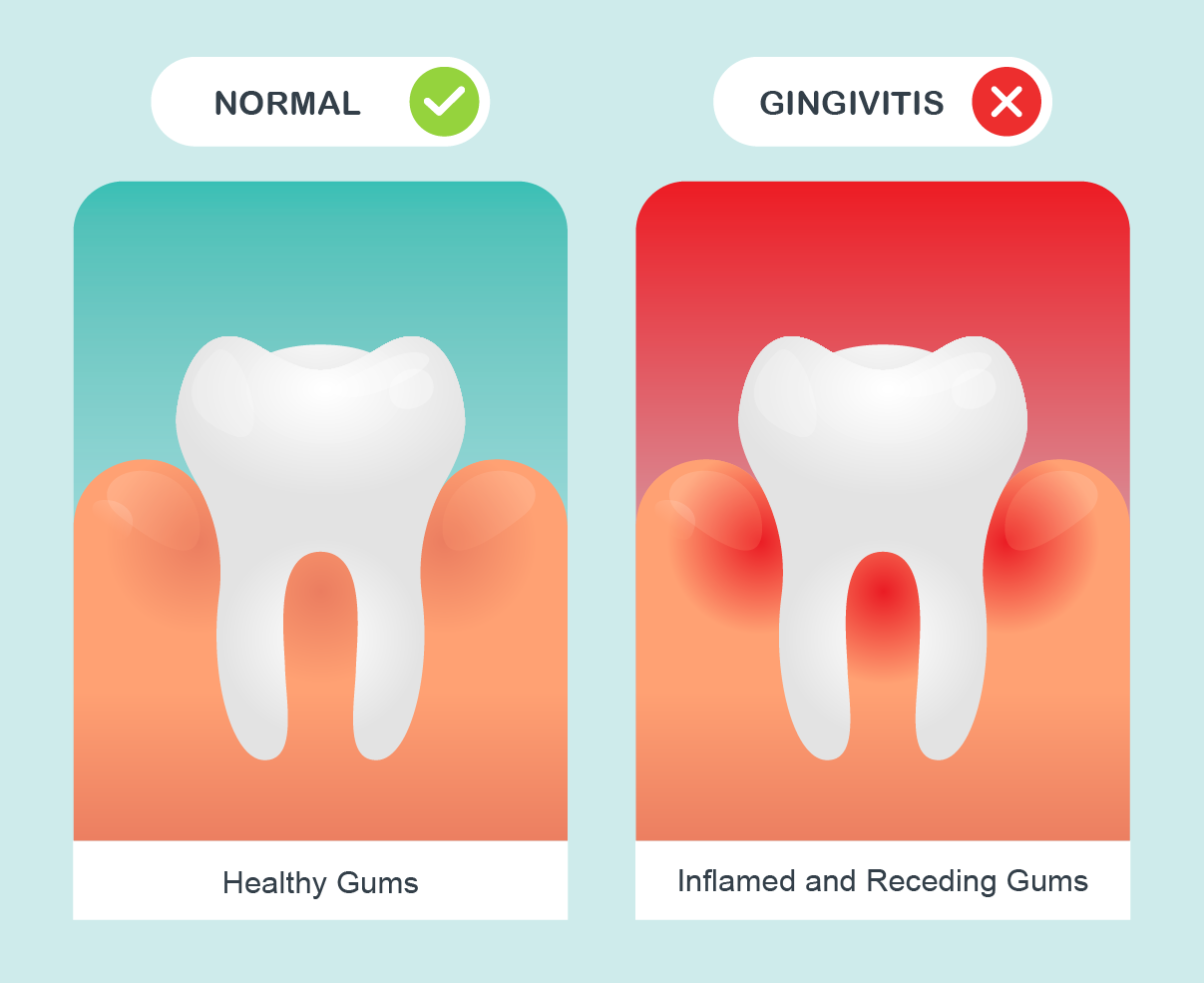
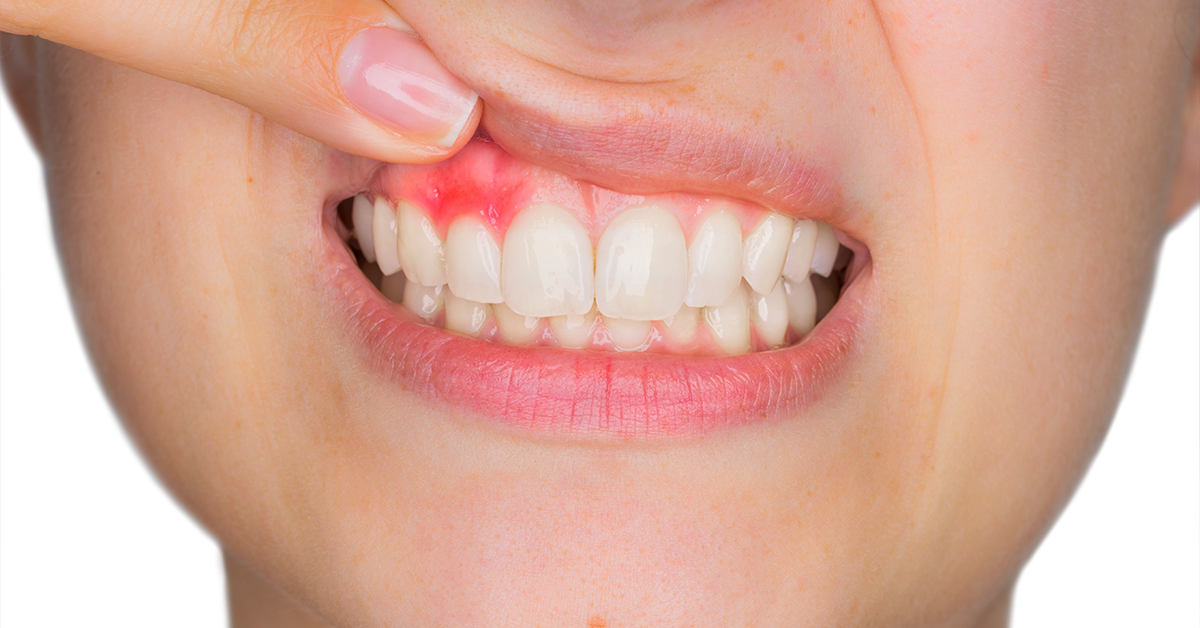
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gingiva (gums), which results in redness, swelling or puffiness of the gums. It is a commonly occurring condition and often known to cause bleeding whilst brushing teeth. The main cause of gingivitis is dental plaque- a sticky film of bacteria that is constantly accumulating on our teeth.
The severity of gingivitis varies depending on the amount of plaque there is, how long it has been there and how much it has spread within the mouth cavity, as well as the overall oral and general health of the individual.
The good news is that gingivitis can be a reversible condition if managed early, and removal of the plaque and bacteria usually result in healing within a short period of time. However, if left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, which is a more serious type of gum infection. This can eventually lead to loss of teeth and other complications, such as recurrent gum abscesses and damage to surrounding structures.
What is tartar?
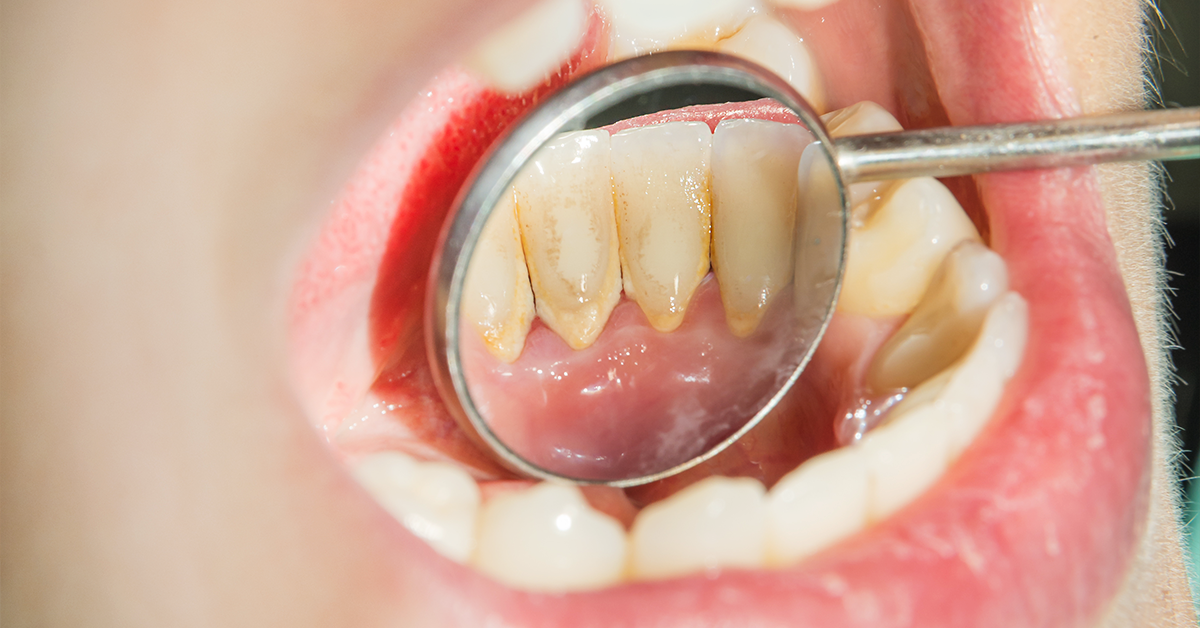
When plaque builds up and hardens, it becomes tartar. Tartar tends to form at the base of the teeth and has a yellow color to it. It is usually formed when plaque is not removed or unable to be removed through regular brushing or flossing. Once formed, it is very difficult to remove tartar through daily cleaning and is best done professionally. If left alone, it can cause further problems such as advanced gum disease and tooth decay.
What are the risk factors for gum disease?

The main cause of gum disease is plaque, but the following factors can also affect the health of the gums:
- Pregnancy — changes in hormone levels during pregnancy can cause the gums to become sensitive, making them more susceptible to inflammation
- Certain conditions — such as cancer, diabetes and HIV have a higher association with gingivitis
- Medications — Some medications like certain anticonvulsants and anti-anginas, may affect the flow of saliva (which plays a significant role in maintaining oral health
- Smoking and high alcohol consumption
- Age — the risk of gingivitis increases with age
- Psychological stress
- Poor sleep
- Poor diet- lacking in vitamins and essential nutrients
- Lack of good oral hygiene Genetic factors
What are the symptoms of gingivitis?
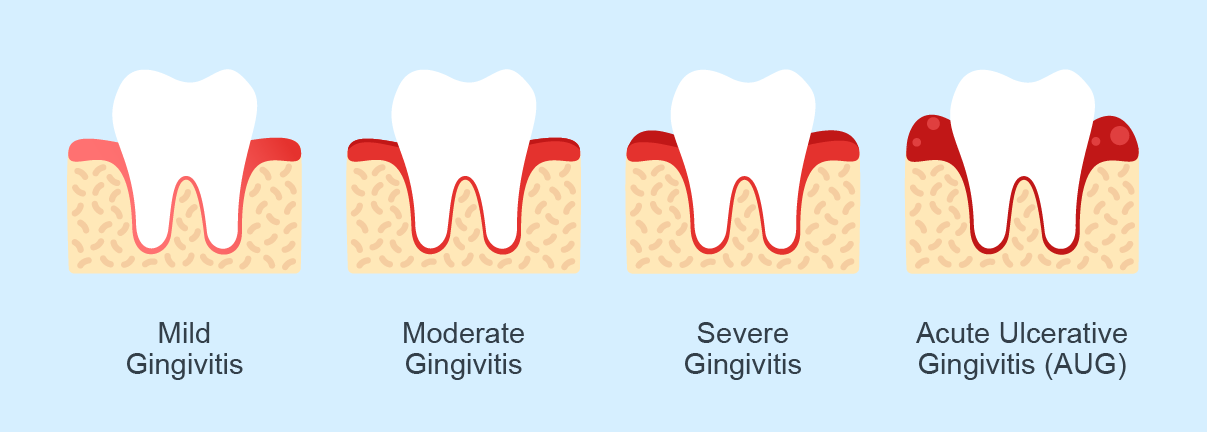
Mild gingivitis: This does not usually cause any symptoms and it may even go unnoticed, apart from the slight swelling or redness of the gums. However, the condition should be taken seriously and addressed sooner rather than later.
Moderate gingivitis: This can cause marked swelling and redness of the gums. the gums can also bleed a little during cleaning. It is not common to feel discomfort or pain at this stage.
Severe gingivitis: The gums at this stage may be very swollen and bleed quite a lot during brushing or flossing. In more severe cases, there may even be bleeding whilst eating. Brushing of the teeth may cause tenderness but it is rarely painful.
Acute ulcerative gingivitis (AUG): This is an acute and severe form of gingivitis. The gums are very swollen, red and ulcerated with AUG. They are also extremely painful to touch, which makes eating quite uncomfortable, and brushing is almost impossible. Individuals with AUG may also have a high fever, painful swollen lymph nodes and a very bad breath. Those who smoke, have poor oral hygiene, a weakened immune system or are under severe stress, are more susceptible to AUG.
Many individuals get quite anxious at the thought of visiting the dentist (known as dental anxiety), and this is more common than we think. However, visiting a dental professional for cleaning and check-ups is a crucial part of oral care, as they can carry out an overall check of the mouth and highlight areas that require attention and treatment. The general recommendation is to have a dental review every 6 months. Those who are more susceptible to gum disease or have risk factors, should try to maintain a higher level of oral care and they may even need to visit the dentist more regularly.
What is the treatment for gingivitis?
Good oral hygiene will help keep plaque levels low, which is essential in preventing and treating gingivitis and its complications such as periodontitis, as well as tooth decay. For daily removal of plaque, it is best to use a soft or moderately soft toothbrush, and ideally an electric one. Studies have shown that the electric brushes with a rotating function are significantly more effective than the manual ones. You should aim to brush your teeth at least twice a day and brush for a duration of around 2 minutes (as that is the approximate time it takes to clean the teeth thoroughly).
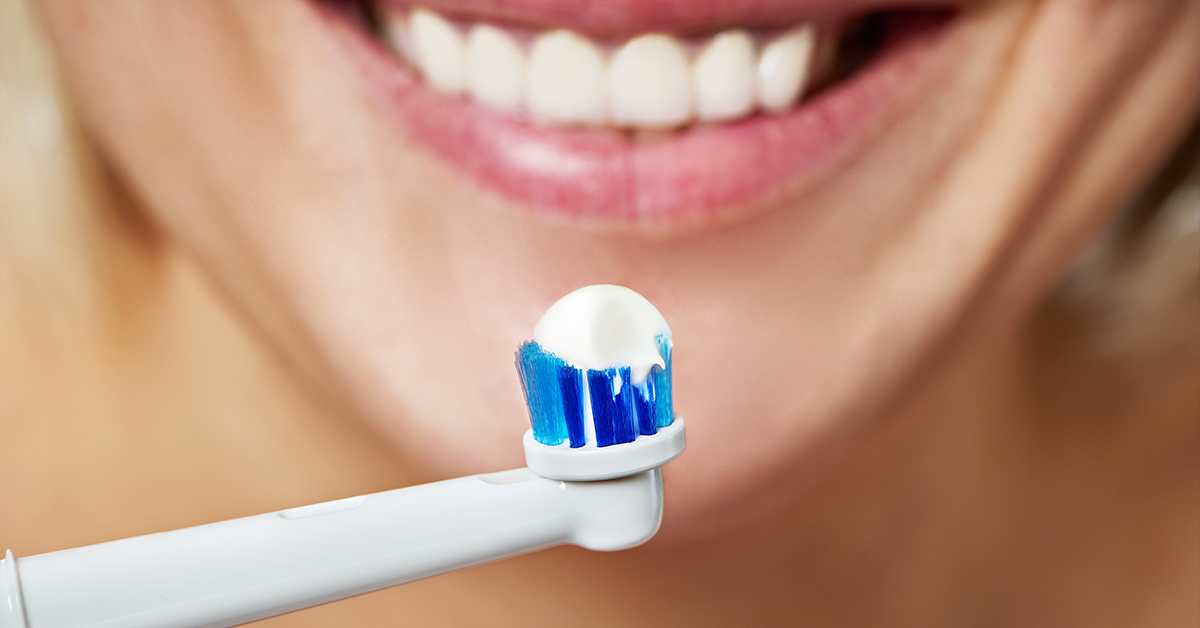

It is very important to also use dental floss and/or interdental brushes daily, as it removes plaque from tooth surfaces that is difficult to remove by simply brushing the teeth.
If your gums bleed when you brush or floss your teeth, try to see where the bleeding is coming from, and be careful when cleaning those areas until the bleeding settles. Bleeding gums is not something to worry about if you have not flossed for some time, as the inflamed gums and plaque have been disturbed, and need some time to heal once the plaque is removed (which usually takes a week). If there is significant or frequent bleeding from the gums, you should get it checked by the dentist to make sure it is not serious or requires any further treatment.
Many individuals get quite anxious at the thought of visiting the dentist (known as dental anxiety), and this is more common than we think. However, visiting a dental professional for cleaning and check-ups is a crucial part of oral care, as they can carry out an overall check of the mouth and highlight areas that require attention and treatment. The general recommendation is to have a dental review every 6 months. Those who are more susceptible to gum disease or have risk factors, should try to maintain a higher level of oral care and they may even need to visit the dentist more regularly.
Professional teeth cleaning by a dental hygienist or dentist can remove stubborn plaque and tartar that is unable to be removed through routine care. Dental tartar may act as an irritant and a reservoir for plaque, leading to gingivitis and gum disease.
Other agents such as mouthwashes and gels can also be used during routine cleaning and may also be advised by your dentist. You can consult your dentist about which one to use if you are not sure.
Plaque is sometimes accumulated within poorly fitted or constructed dental fillings, crowns, and prosthetic appliances, despite adequate regular cleaning. Correction of such dental restoration and prosthetic devices should be carried out by a dentist to enable effective removal of plaque and reduce the risk of gum disease.
Cleaning of the equipment and its storage is not to be missed either. Toothbrushes should be rinsed well after each use and kept in a clean and dry place, and they should be replaced every 3 to 4 months. Interdental brushes should also be rinsed after use and replaced every 1 to 2 weeks.
What are the complications associated with gingivitis?
If left untreated or inappropriately managed, gum disease has a potential to spread and cause complications, affecting the teeth as well as other tissues and bones. These complications include:
- Abscesses or infection of the gums or jawbone
- Periodontitis – which is more serious than gingivitis as it can lead to loss of teeth
- Recurrent gingivitis
- Serious infections and ulceration of the gums
As mentioned previously, gum diseases have also been linked to other conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes (although it has not been shown to directly cause them). More research is still required to determine the specifics of these associations.
The take home message….
Gingivitis is a reversible condition that can be managed well. It does however require early treatment and care, as it is linked to complications that can be serious and even devastating for individuals, such as loss of teeth. There are lots of effective ways to prevent and manage this condition, and it is important to start as early as possible.

Part of its management is the daily oral care at home, through brushing and flossing regularly. This also includes avoiding any preventable risk factors that can increase the risk of getting gum disease. The other part is to get regular check-ups by the dentist, as they can highlight any areas that may need treatment and give advice on how to effectively take care of the oral cavity.
Halza has great features to help you stay on top of your health. With regular appointment reminders and medication alerts, you can be stay well organized. You can also store and share any test results and images (such as X-rays) with other professionals.